Terms
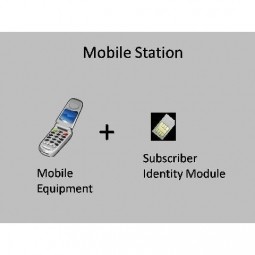  |
Mobile Station
A mobile station comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network. The term refers to the global system connected to the mobile network. |
  |
Mobile Station ISDN
Mobile Station ISDN (MSISDN) is a number uniquely identifying a subscription in a GSM or a UMTS mobile network. The MSISDN, together with IMSI are two important numbers used for identifying a mobile subscriber. |
  |
Mobile Virtual Network Operator
Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) is a mobile operator that does not own spectrum or have its own network infrastructure. An MVNO has business arrangements with traditional mobile operators to buy network time, which it then sells to its own customers. |
  |
Modbus
Modbus is an open and widely used de facto standard applied in a large number of application areas, such as the industrial sector, buildings, traffic, and energy. |
  |
Molecular Sensor
A molecular sensor or chemosensor is a molecule that interacts with an analyte to produce a detectable change. Molecular sensors combine molecular recognition with some form of the reporter, so the presence of the guest can be observed. |
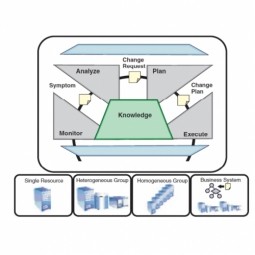  |
Monitor-Analyze-Plan-Execute-Knowledge
Monitor-Analyze-Plan-Execute-Knowledge (MAPE-K) control loop was first introduced by IBM in their white paper: "An architectural blueprint for autonomic computing." It collects the details from the managed resources. |
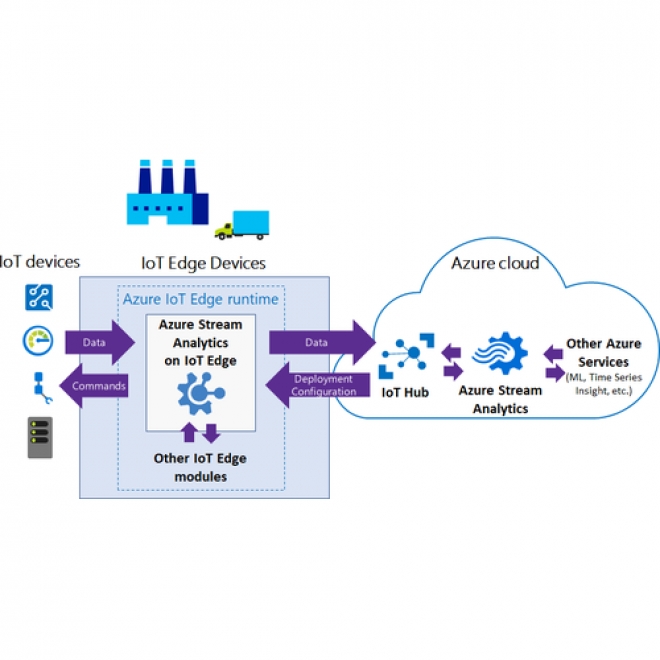  |
Monitoring & Stream Analytics
Monitoring and stream analytics compare and analyze data that are available to the smart factory from diverse sources – devices, sensors, infrastructure, etc. |
  |
Mote
Short for Remote - a mote is a wireless transceiver that also acts as a remote sensor. The ability to log onto a network from a distant location. Generally, this implies a computer, a modem, and some remote access software to connect to the network. |
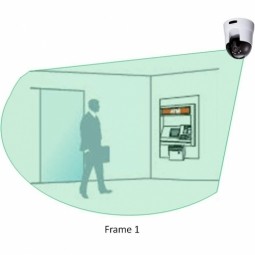  |
Motion Detection
Infrared motion sensors that reliably send alerts to alarm panel (or dialer) and with a system implementing reduced false alarms algorithms and adaption to environmental disturbances. |
  |
Multiple DoF Sensing
A MEMS concept referring to the detection of the combined input along multiple axes using multiple sensing types, such as acceleration and rotation. Typical applications include antenna stabilization, robotics, and dead-reckoning. |
  |
Multiple Input, Multiple Output
The input-output concept in the context of antennas. A radio technology using multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. MIMO is an important part of wireless communication standards, such as IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi). |
|
Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy is a kind of software operation model where a single instance of a software application servers multiple users. Each customer/organization is called a tenant. |
|
  |
Nanotechnologies
Nanoscience and nanotechnology are the study and application of extremely small things and can be used across all the other science fields, such as chemistry, biology, physics, materials science, and engineering. |
  |
Natural Langauge Processing
The software that enables humans to interact naturally with technology and machines. Advances in natural language processing (NLP) and speech recognition are making it much easier for humans to interact naturally with technology and machines―and companies are starting to recognize this value. |
  |
Nearables
Coined for the similarity to “wearables,” this describes items with nearby tracking devices, or beacons, attached to them. Nearables can communicate with smart devices, such as smartphones, to let the user interact with objects in their vicinity. |
  |
Near Field Communication
A protocol that enables smartphones and other devices to establish radio communication with each other by close proximity. (Near Field Communication) NFC has been overshadowed in IoT applications by other protocols such as BLE. |
  |
Network Security
A connected factory requires the use of standard communication protocols to enable machine-to-machine communication. As a result, secure, reliable communication and sophisticated identity and access management of machines and users are essential. |
  |
Not Only SQL
A broad class of database management systems. Not Only SQL (NoSQL) database, is an approach to data management and database design that's useful for very large sets of distributed data. |
  |
On-Board Diagnostic Port
On-Board Diagnostic Port (OBD) systems give the vehicle owner or repair technician access to the status of the various vehicle subsystems. The amount of diagnostic information available via OBD has varied widely. |
  |
On-Board Equipment
Components of a Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) implementation located in a moving vehicle, communicating wirelessly with roadside equipment (RSE). On-Board Equipment (OBE) applications may interface with other vehicle systems via the CAN Bus. |
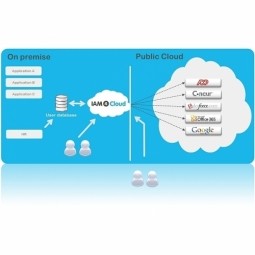  |
On-Premise
On-premises software is installed and runs on computers on the premises (in the building) of the person or organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility, such as at a server farm or cloud - somewhere on the Internet. |
  |
Open Source
A type of software where the source code is available and can be modified and freely redistributed. Open source code is typically created as a collaborative effort in which programmers improve upon the code and share the changes within the community. |
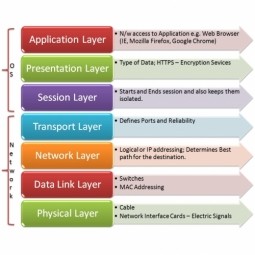  |
Open Systems Interconnection Model
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to their underlying internal structure and technology. |
  |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition (OCR) or optical character reader is the mechanical or electronic conversion of images of typed, handwritten, or printed text into machine-encoded text. |
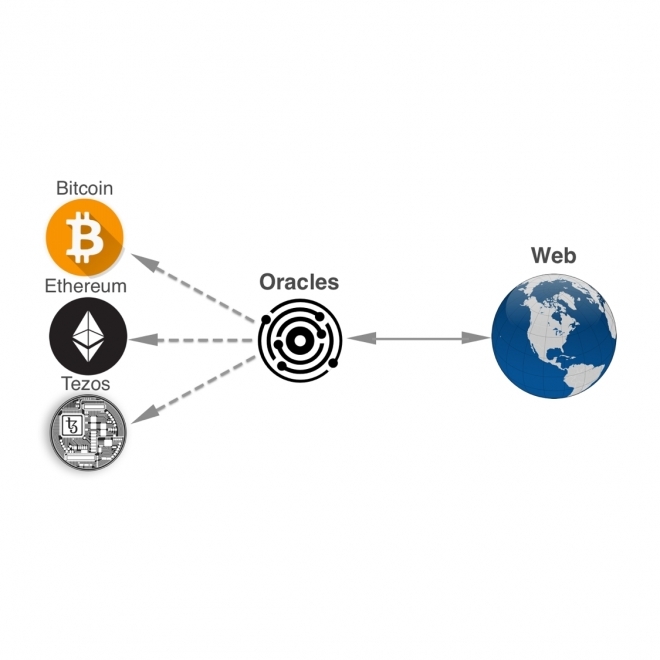 |
Oracles
An oracle is a way for a blockchain or smart contract to interact with external data. With blockchains being deterministic one-way streets, an oracle is a path between off-chain and on-chain events. |
  |
Orchestration
Orchestration describes the automated arrangement, coordination, and management of complex computer systems, middleware, and services. Type of composition where one particular element is used by the composition to oversee and direct the other elements. |
  |
Outcome Economy
An economic relationship in which payment is attached to a value achieved, rather than a service or product. Digital devices on edge are powering an Outcome Economy and enabling a new business model that shifts the focus from selling things to selling results. |
  |
Paper Based Batteries
A paper battery is an electric battery engineered to use a spacer formed largely of cellulose (the major constituent of paper). Paper-based batteries incorporate nanoscale structures to act as high surface-area electrodes to improve conductivity. |
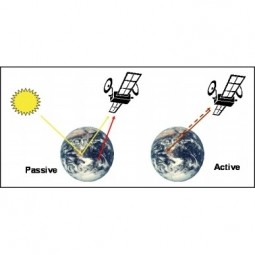  |
Passive Sensor
A passive sensor is a device that detects and responds to some input from the physical environment. Passive sensor technologies gather target data through the detection of vibrations, light, radiation, heat, or other phenomena occurring in the subject’s environment. |
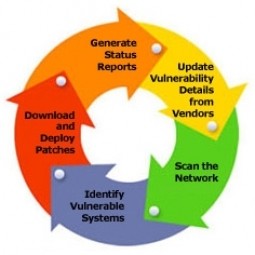  |
Patch Management
Patch management is an area of systems management that involves acquiring, testing, and installing multiple patches (code changes) to an administered computer system. |
