Technology Category
- Analytics & Modeling - Real Time Analytics
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
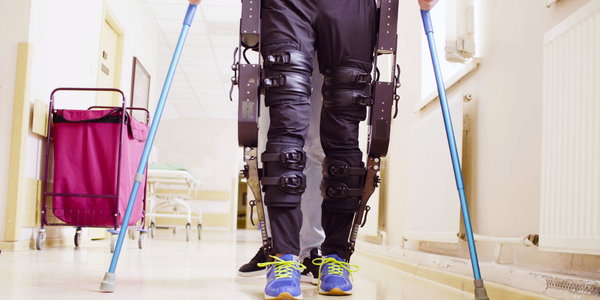
- Wearables - Exoskeletons
Applicable Industries
- Automotive
Applicable Functions
- Product Research & Development
The Customer
Hyundai Motor Company
About The Customer
Hyundai Motor Company
The Challenge
The Central Advanced Research and Engineering Institute at Hyundai Motor Company develops future mobility technologies. Rather than provide conventional vehicle products to customers, this research center creates new mobility devices with a wide range of speeds for a variety of people, including the elderly and the disabled. As our society ages, there is a greater need for systems that can aid mobility. Thus, we are developing wearable exoskeleton robots with NI embedded controllers for the elderly and patients with spinal cord injuries to use.
Key Challenge
Developing a system that can handle complex control algorithms to capture data remotely from various sensors simultaneously and perform real-time control of multiple actuators for a wearable robotics device for walking assistance.
The Solution
Using the LabVIEW RIO platform, including a CompactRIO embedded system and a real-time controller with an FPGA control architecture provided by Single-Board RIO, to acquire data from various sensors and control peripheral units, high-speed communication devices, and actuators; and using LabVIEW software to acquire reliable data by conducting real-time analysis and applying various robot control algorithms to dramatically reduce development time.

Case Study missing?
Start adding your own!
Register with your work email and create a new case study profile for your business.
Related Case Studies.

Case Study
Integral Plant Maintenance
Mercedes-Benz and his partner GAZ chose Siemens to be its maintenance partner at a new engine plant in Yaroslavl, Russia. The new plant offers a capacity to manufacture diesel engines for the Russian market, for locally produced Sprinter Classic. In addition to engines for the local market, the Yaroslavl plant will also produce spare parts. Mercedes-Benz Russia and his partner needed a service partner in order to ensure the operation of these lines in a maintenance partnership arrangement. The challenges included coordinating the entire maintenance management operation, in particular inspections, corrective and predictive maintenance activities, and the optimizing spare parts management. Siemens developed a customized maintenance solution that includes all electronic and mechanical maintenance activities (Integral Plant Maintenance).

Case Study
Monitoring of Pressure Pumps in Automotive Industry
A large German/American producer of auto parts uses high-pressure pumps to deburr machined parts as a part of its production and quality check process. They decided to monitor these pumps to make sure they work properly and that they can see any indications leading to a potential failure before it affects their process.







